While a lot of businesses have heard about Twitter, they’re confused about how to best leverage it for their own businesses – or they don’t think it’s applicable to their business model at all. To clear up some of the confusion and help you understand how your company can utilize Twitter, we’re going to a short series on Twitter as a marketing channel for businesses. This first part of the series is just going to provide a breakdown of the basics before we delve into the nitty gritty.
What Is Twitter?
Started in 2007, Twitter has experienced exponential growth over the last few years and has created a new way in which businesses can reach out to current and potential customers. Like most social medial platforms, Twitter is composed of user-generated content. Users can post text messages that are 140 characters or fewer. Each of these text messages is called a tweet. Tweets can be seen by a group of interested recipients known as followers. Every account has a username, which is also called a Twitter handle. All Twitter handles are denoted by the @ symbol. For example, our Twitter handle is @digitaldogsaz.
Twitter Lingo
There are a lot of new terms that come with any new technology. Part of what keeps some companies from using Twitter is simple confusion as to what these terms mean. Here, we define the most commonly used phrases.
Tweet: A message of up to 140 characters sent via Twitter. You can use the word tweet as a noun, such as “I sent a tweet about our new product line this morning,” or as a verb, such as “I tweeted about our March promotion.” You can also refer to a tweet as a post, message, or an update.

Hashtag #: A hashtag is the # symbol that’s followed by a phrase that describes the topic of the tweet. For instance, if you were tweeting about the 2012 Olympics, you would incorporate a hashtag such as #london2012 or #olympics. Using a hashtag helps users understand that your message is about the same topic as other tweets that contain the hashtag. Users can search for specific hashtags and see a list of all related posts. Companies can use hashtags for new product launches (e.g., #GiletteMach3) or for conferences and events.
Following/Followers: You receive messages on Twitter by following people or companies in which you’re interested. Once you start following someone, their messages will appear in your incoming timeline on your Twitter homepage. Likewise, to get your tweets seen by other people, you have to garner followers to your account.

Direct Message: Direct Messages, also known as DMs, are messages sent through Twitter’s private messaging channel. These tweets will appear under the “Messages” tab on your homepage. If you have email notifications turned on, you’ll also receive an email message when someone sends you a DM. Only you can see DMs sent to you – they don’t appear in search results or in your public timeline. You can only send DMs to people who are following you (and, conversely, you can only receive DMs from people you follow). There are a couple of ways you can send DMs. You can go to your “Messages” tab, use the pull-down menu to select a recipient, and start typing your tweet. You can also send DMs from your Twitter homepage by typing “d username” and then your message. For example, if you wanted to contact us, you would type, “d digitaldogsaz I have a question about using Twitter.”
ReTweet (RT): You can quickly share other people’s ideas or praise someone’s work on Twitter by reposting their tweets and giving them credit. Known as “retweeting” (RT), it typically looks like this: RT @Username: Original message (often with a link.” Retweeting occurs commonly on Twitter, and it provides an effective way for quickly spreading messages and ideas.
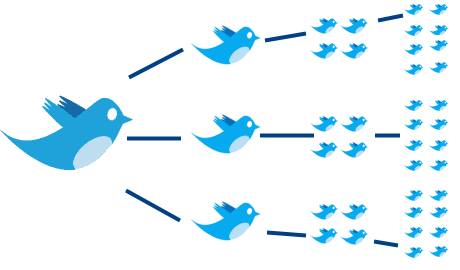 With retweets, your company’s message can quickly spread to a new audience.
With retweets, your company’s message can quickly spread to a new audience.
Twitter Handle: The username for your Twitter account. Twitter handles are denoted by the @ symbol, so they appear like this: @digitaldogsaz.
In the next part of our series, how Twitter can be used in the business world and why it might (or might not) be a good fit for your company’s marketing efforts.
Have any questions? Let us know in the comment section below.
Read More